IEC 62366 Explained: What You Need To Know About Usability Engineering
Usability engineering (UE)—or human factors engineering (HFE), as it’s also known—is focused on designing a user interface (UI) that allows people to quickly understand how to interact with a product in the most efficient and error-free manner.
When we say a product is “intuitive” or “user friendly” we’re referring to its usability; however, this doesn’t just apply to the apps on your phone. Common household items like your microwave, television remote, and even your car are all designed with human factors in mind.
Usability engineering is also a high priority in the medical device industry. Devices that lack an intuitive design and fail to take into account the user-device interaction can jeopardize patient and user safety.
Fortunately, regulatory bodies have long understood this problem, and have created a number of regulations and standards to help guide medical device manufacturers in the usability engineering process.
Today, we’ll be focusing on one of those standards in particular: IEC 62366.
What is IEC 62366?
IEC 62366 is the international standard that covers the application of usability engineering to medical devices. This standard helps medical device manufacturers consider human factors by offering a standardized process for analyzing, specifying, developing, and evaluating the usability of their medical device.
IEC 62366 is broken into two parts:
-
IEC 62366-1 — Application of usability engineering to medical devices
-
IEC 62366-2 — Guidance on the application of usability to engineering to medical devices
IEC 62366-2 is a technical report which contains background information and guidance on implementing IEC 62366-1 and does not specify any requirements.
The most recent versions of these two parts of the standard are IEC 62366:2015 + A1:2020 and IEC 62366-2:2016, and they are recognized consensus standards by FDA. This means FDA will accept a “declaration of conformity” from a medical device manufacturer to satisfy part of a premarket review requirement.
What is the usability engineering process from IEC 62366?
The usability engineering process found in IEC 62366 consists of a series of steps to ensure that the UI of a medical device has been rigorously evaluated for user and patient safety:
-
Define intended users, use environments, and user interface.
-
Identify use-related hazards.
-
Identify and categorize critical tasks.
-
Develop and implement risk mitigation/control measures.
-
Validate user safety and effectiveness.
-
If validation shows that use-related risks are unacceptable, or that new use-risks have been introduced, you must return to the previous step and implement effective risk control measures.
-
Document your UE process.
It’s important to note that usability engineering validation of devices takes two forms, formative evaluations and evaluations.
Formative evaluations
Formative evaluations are conducted while a device is still in design and development. These evaluations are used to address safety concerns that emerge during preliminary analyses or to explore different design options for the UI before it’s finalized. You may end up carrying out multiple formative evaluations.
Summative evaluations
Summative evaluations are conducted during the design validation stage of a device. A summative evaluation is much more rigorous than a formative evaluation, as its goal is to demonstrate that the UI is safe for users. Testing should involve the intended end users of the device engaging with the final UI design under realistic conditions.
Usability Engineering is key to understanding the intent of IEC 62366
The goal of usability engineering is to identify and mitigate any use-related hazards and risks, and to create a UI that encourages error-free use of the device. In the medical device industry, the user may be a doctor or other healthcare provider, but in some cases the device may also be operated directly by a patient with no clinical background.
Usability engineering requires the analysis of the interaction between the intended user and a device, including:
-
The information users perceive from the device, as well as its labeling, packaging, and instructions.
-
How users interpret that information to make decisions regarding the operation of the device.
-
How they use the device—manipulating its components, controls, settings, etc.
It’s also essential to consider the opposite transfer of information: from the user to the device.
-
How does the device receive inputs from the user?
-
How does the device respond to the user and provide feedback about the effects of their decision to manipulate the device in a specific manner?
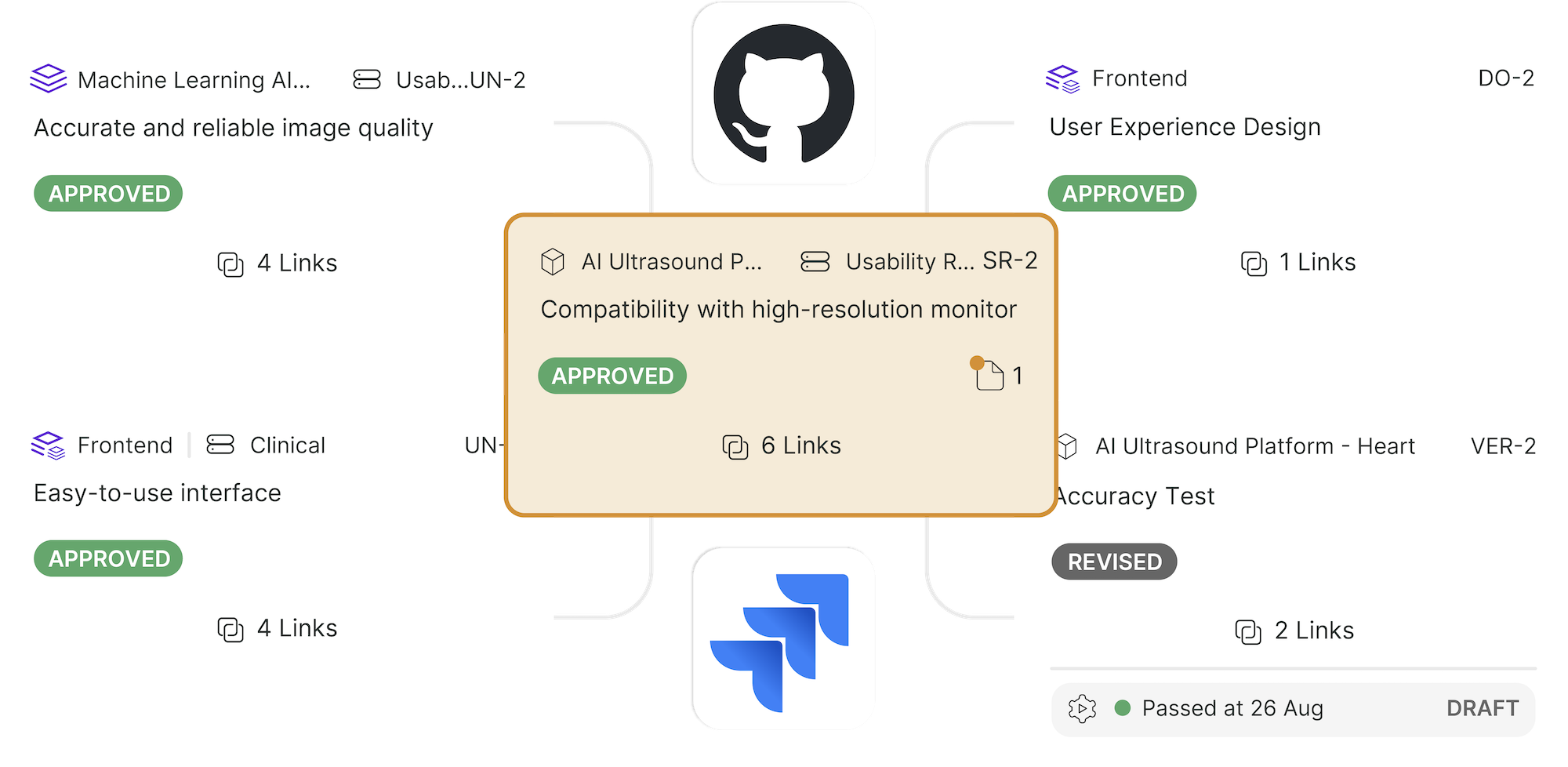
The image below shows this continuous flow of information between the user and the device.
 Device User Interface in Operational Context (Redmill and Rajan, 1997)
Device User Interface in Operational Context (Redmill and Rajan, 1997)
Design issues, with either software or hardware, have long been one of the leading causes of medical device recalls. However, as the reliance on software in medical devices has grown, the need for rigorous UE processes has increased substantially. One study found that between 2012 and 2015 alone, there were 423 medical device recalls resulting from UI software errors.
When usability engineering is done properly, it has a host of benefits for both users, patients, and medical device companies. Devices become easier to use, which results in the reduced risk of use error, adverse events, and product recalls.
Follow IEC 62366 best practices for better usability with Greenlight Guru
You may have noticed that the UE process from IEC 62366 has a lot of steps in common with design controls and risk management. That’s not a coincidence. Usability engineering is not a separate set of steps to be performed outside of your design control or risk management activities. They are all inextricably connected.
That’s one of the reasons it makes so much sense for a medical device company to use a QMS built specifically for the medical device industry. Greenlight Guru's QMS software integrates all of your design, risk, and quality processes for seamless usability engineering that aligns with industry best practices, like IEC 62366.
Get your free demo of Greenlight Guru today!
Looking for a design control solution to help you bring safer medical devices to market faster with less risk? Click here to take a quick tour of Greenlight Guru's Medical Device QMS software
Etienne Nichols is the Head of Industry Insights & Education at Greenlight Guru. As a Mechanical Engineer and Medical Device Guru, he specializes in simplifying complex ideas, teaching system integration, and connecting industry leaders. While hosting the Global Medical Device Podcast, Etienne has led over 200...
Related Posts
Understanding The Relationship Between Usability and Labeling of Your Medical Device
3 Common Problems with Design Controls (and the Solutions)
3 Life[cycle] Hacks for Integrating Risk Management throughout all Device Phases
Get your free template
Human Factors & Usability Engineering Report Template + Checklist