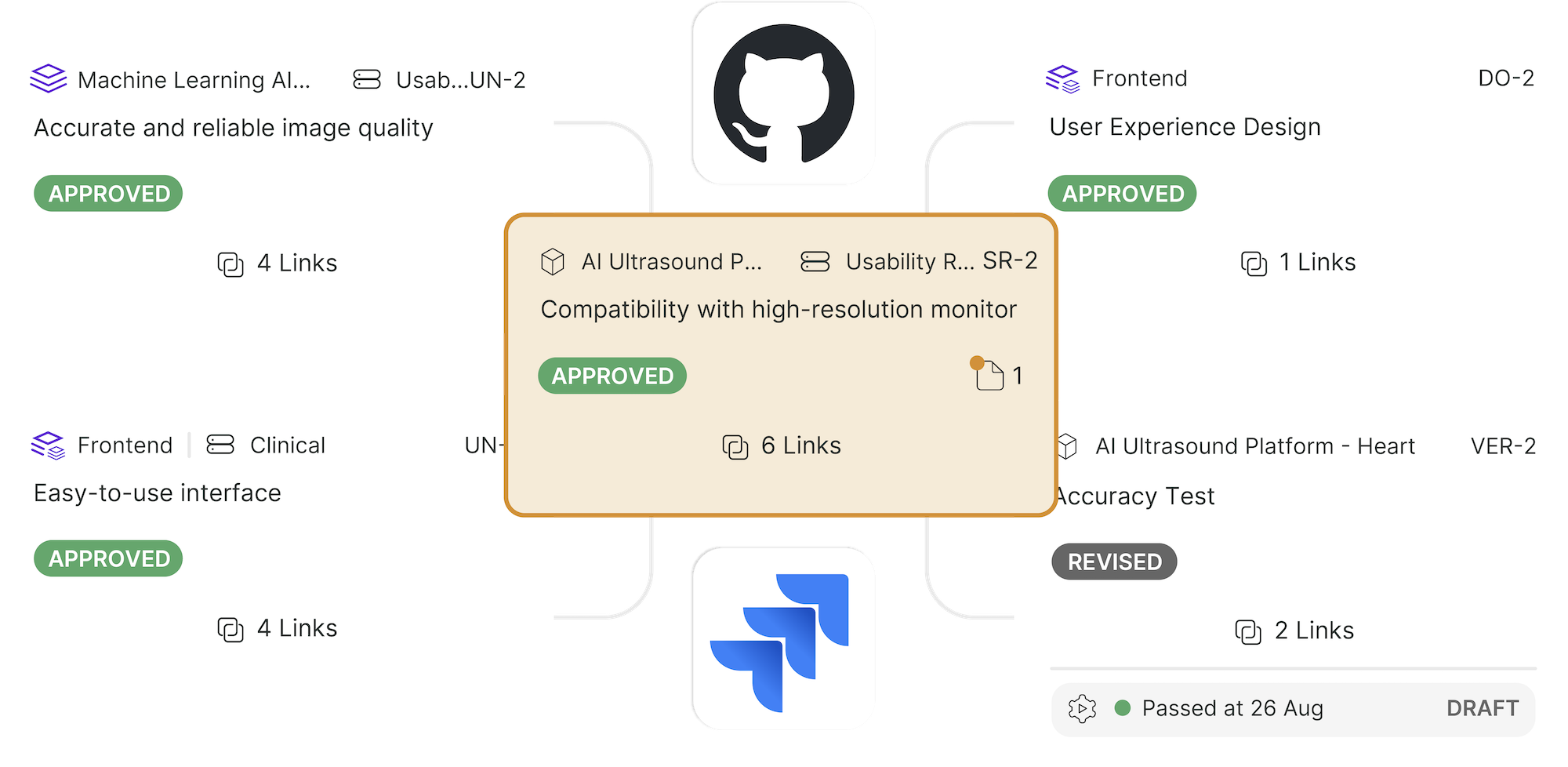
How the Design Control Process Applies to a 510(k) Premarket Notification
%20Premarket%20Notification.png?width=860&name=How%20the%20Design%20Control%20Process%20Applies%20to%20a%20510(k)%20Premarket%20Notification.png)
At its core, the 510(k) Premarket Notification pathway comes down to assuring regulators that your medical device is safe and effective.For many medical device companies, what constitutes “safe and effective” can cause undue confusion. But the question of how to prove these rather-broad sets of criteria can actually be answered by following one process: design controls.
Design controls are the most effective form of documented, objective proof that you have designed a safe product that meets user needs and regulatory requirements. During this process you will define design inputs and design outputs, establish standards for quality, incorporate a risk-based approach, and connect every component of the device back to end users.
Keep reading to learn how design controls connect to your 510(k) by understanding the different sections of a 510(k) submission and when and where your design controls fit into the process.
Is it possible to draft a 510(k) submission without a design control process?
Throughout my career, I have believed the answer to that question to be an emphatic “no”. However, more recently, I have come across many, many examples of companies and individuals who have submitted 510(k)s and documented no design controls.
It blows my mind that somebody would consider submitting a 510(k) without having design controls documented in a design history file.
Why? To me, there is no way to construct a 510(k) submission without design controls.
Whenever I have worked on completing a 510(k) submission, I start first by establishing the design controls and DHF. I actually use the contents of a DHF to guide the preparation of a 510(k) submission. In fact, documenting and organizing design controls in a DHF should be the first step taken in preparing a 510(k) submission.
Once you get FDA 510(k) market clearance, you will be subject to inspection by FDA. It may not happen immediately after getting clearance. However, you should anticipate that an inspection will happen since FDA has a mandate to do so at least every two years for medical device companies with Class II and Class III products.
And year after year, design controls are cited as a top issue during FDA inspections.
Doesn’t it make logical sense to ensure and establish that design controls are captured and documented before you actually submit that 510(k)?
Understanding the role of your design control process in a 510(k) submission
A successful 510(k) submission process rests on these following two pillars:
- Demonstrating a device to be substantially equivalent to a predicate device
- Establishing a thorough risk mitigation plan
Design controls play a massive role in both of these requirements. By focusing on design controls in your 510(k) submission, you’ll be able to easily compile the necessary documentation and assets needed to demonstrate substantial equivalence to predicate devices and the foundation of a thorough risk management plan.
Let’s zoom in on both sides of the proverbial 510(k) submission coin to see how design controls can bolster your claims for substantial equivalence and a competent risk mitigation strategy.
How do design controls help with demonstrating substantial equivalence?
Demonstrating substantial equivalence to a predicate device establishes a standard to which a device can be compared.
This is extremely helpful to both manufacturers and FDA officials alike; medical device companies can use them during product validation and verification, and FDA investigators can easily understand a device’s potential at a glance.
While the FDA view of predicate devices is somewhat vague, they do provide a valuable piece of guidance on substantial equivalence. In this guidance document, the agency recommends that medical device manufacturers choose a predicate device that is most similar with regard to intended use and technological characteristics.
Establishing a device’s intended use and indications of use is quite literally a part of the design control process. These definitions help to determine key factors like:
-
User needs have been met
-
Human and environmental factors have been considered
-
All user groups have been identified
-
Validation you’ve built the right product
-
Verification you’ve built the product right
Additionally, separate FDA guidance points to another application of design controls, specifically the labeling and packaging steps required for 510(k) submissions.
Section 513(i)(1)(E) of the Act generally limits the determination of the intended use of a device that is the subject of a premarket notification (510(k)) to the proposed labeling contained in the submission.
When they refer to labeling, this includes:
-
Labels that are affixed to the device,
-
Labels on packaging,
-
Any inserts within the packaging
-
Any advertising or promotional materials such as your website.
FDA will evaluate all labeling to determine the intended use of the medical device and additionally, whether it is substantially equivalent to a predicate device.
How does the design control process connect to risk mitigation?
Design controls are intended to demonstrate that a medical device has been:
-
Designed to address the needs of users and patients.
-
Designed to meet inputs and requirements.
-
Proven to meet applicable standards.
-
Meets performance criteria.
If you are thorough with defining and documenting user needs, design inputs, design outputs, design verification, design validation, and design reviews, then you will be on the right track towards ensuring your medical device is safe.

The best practices of medical device product development have a good flow between design controls and risk management. For example, as you identify hazards and hazardous situations, these should “feed” into the design controls process in defining user needs and design inputs.
Prior to clinical use, you have to know without a doubt that the product is safe and/or determine that the medical benefits outweigh the risks, which should be documented in a benefit/risk analysis.
Which parts of a 510(k) submission apply to the design control process?
At least fourteen of the twenty sections of FDA’s 510(k) submission requirements relate to your design controls. Below, I will explain the specific sections of a 510(k) submission that incorporate design controls.
Section 4.0: Indications for Use Statement
FDA describes the indications for use statement as:
The statement should include specific indications, clinical settings, define the target population, anatomical sites, etc. This statement must be consistent with your labeling, advertising and instructions for use.
Your indications for use describe the entire purpose for your medical device. This statement then feeds into establishing user needs for your product.
Furthermore, user needs initiate the design control process. User needs are the primary basis for establishing your design inputs. Towards the end of your development efforts, user needs also play a significant role. Design validation demonstrates the product you have developed meets the user's needs.
Section 5.0: 510(k) Summary
The 510(k) summary is an overview of your medical device. The 510(k) summary includes:
-
A description of the device according to the product labeling (relates to design outputs)
-
Explanation of how the device functions (relates to design inputs)
-
Physical and performance characteristics including device design, materials, and physical properties (relates to design inputs)
-
Predicate device comparison via technological characteristics and testing (relates to design inputs, design outputs, and design verification)
-
Summary of nonclinical testing (or clinical testing, if applicable) (relates to design verification)
These items are a combination of design inputs, design outputs, and design verification activities.
Section 9.0: Declarations of Conformity and Summary Reports
In this section, FDA outlines its requirements for manufacturers to provide declarations of conformity to any standards followed. For some device types, there may be applicable performance standards to follow during the product development process, such as IEC 60601-1 and ISO 10993. Criteria contained within standards, such as these, often relates to design inputs as well as design verification.
Section 10.0: Executive Summary
The executive summary section comprises a culmination of indications for use (section 4.0), device description (§ 11.0), device comparison (§ 12.0), and performance testing (§ 18.0, § 19.0, and § 20.0). There are elements of user needs, design inputs, design outputs, design verification, and design validation included in the executive summary.
Section 11.0: Device Description
The section for device description includes details relating to your design inputs and design outputs. Section 11.0 can often be fairly detailed and include drawings and schematics to help explain your product in your 510(k) submission to FDA.
Section 12.0: Substantial Equivalence Discussion
In this section, you are comparing your medical device to the predicate product. This substantial equivalence discussion will primarily focus on specific product characteristics (design outputs) and side by side comparison, often in the form of testing (design verification).
Section 13.0: Proposed Labeling
Proposed labeling includes the labels included on your product and packaging, as well as instructions for use and operator manuals. Labeling should be described and captured as design outputs.
Section 14.0: Sterilization and Shelf Life
Design inputs should describe sterilization methods, identify specific sterilization parameters, describe packaging criteria, and shelf life. Your design verification activities must be able to demonstrate these inputs have been met. This will include sterilization validation and shelf life testing.
Section 15.0: Biocompatibility
Biocompatibility closely relates to design inputs and design verification, as your design inputs must describe type of body contact and duration. Additionally, design verification must demonstrate the materials are safe and effective and meet the established biocompatibility design inputs.
Section 16.0: Software
If your device contains software, this section of your 510(k) submission will contain software-related design inputs, design outputs, and design verification activities.
Be prepared to follow the FDA guidance on Content of Premarket Submissions for Software Contained in Medical Devices and provide documentation described within this document.
Section 17.0: Electromagnetic Compatibility and Electrical Safety
If your medical device has electronic components, this section must contain evidence to support electrical safety. This relates to design inputs, design outputs, and design verification.
I suggest familiarizing yourself with the industry IEC standards for electrical safety to ensure you are designing for compliance with IEC 60601 in order to avoid any hiccups during the 510(k) submission review process.
Section 18.0: Performance Testing – Bench
Any “bench” testing conducted as part of product development efforts must be summarized in this section of your 510(k) submission. This relates to design verification activities.
Section 19.0: Performance Testing – Animal
Any “animal” testing conducted as part of product development efforts must be summarized in this section of your 510(k) submission. This often relates to design verification activities and sometimes design validation.
Section 20.0: Performance Testing – Clinical
Any “clinical” testing conducted as part of product development efforts must be summarized in this section of your 510(k) submission. This often relates primarily to design validation.
Connect your design control process to every part of your product with Greenlight Guru
510(k) submissions need documentation of the design control processes in order to be successful. So, wouldn’t it make sense to dedicate the same due diligence throughout the entirety of your medical device’s lifecycle?
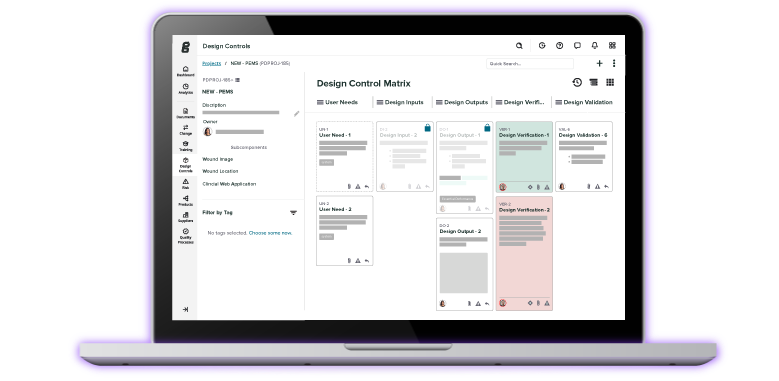
With Greenlight Guru’s dedicated Design Control Software, you can easily achieve 21 CFR Part 820.30 and ISO 13485 compliance with an auto-generating, auto-updating DHF. Our end-to-end platform eliminates data silos, so you can create and update your traceability matrices and schedule a design review in mere minutes — not hours or days. More than that, our solution ensures full visibility and connectivity between your inputs, outputs, verifications, and validations related design inputs, risk controls, and components.

Want to see it in action? Contact us today to get a deep dive into our Design Control Software, ask questions, and see your multi-level design control matrix come to life.
Etienne Nichols is the Head of Industry Insights & Education at Greenlight Guru. As a Mechanical Engineer and Medical Device Guru, he specializes in simplifying complex ideas, teaching system integration, and connecting industry leaders. While hosting the Global Medical Device Podcast, Etienne has led over 200...
Related Posts
The Ultimate Guide To Design Controls For Medical Device Companies
Design History File (DHF) vs. Device Master Record (DMR) vs. Device History Record (DHR): What's the Difference?
FDA 510(k) Submission Process: A Step-By-Step Guide On How To Prepare Yours
Get your free PDF
Design Control & DHF Table for 510(k) Submissions